Men's Blue
Balance – Menopause Support
Balance – Menopause Support
Couldn't load pickup availability
Balance – Menopause Support is a comprehensive women’s health formula designed to help support hormonal balance, digestive health, mood stability, energy, and overall well-being during menopause. With a synergistic combination of vitamins, probiotics, prebiotics, and botanical extracts, this formula delivers targeted nutritional support to help women feel their best through every stage of menopause.
Our product is synthesized utilizing the latest scientific research and formulated with efficacious dosages to promote optimal results. Balance – Menopause Support combines traditional herbal wisdom with modern nutritional science to deliver a premium formula produced under the most stringent quality protocols.
This formula is third-party independently tested for purity and potency, manufactured in the USA, GMP certified, and produced in an FDA registered facility. Very few menopause support products on the market meet these world-class standards.
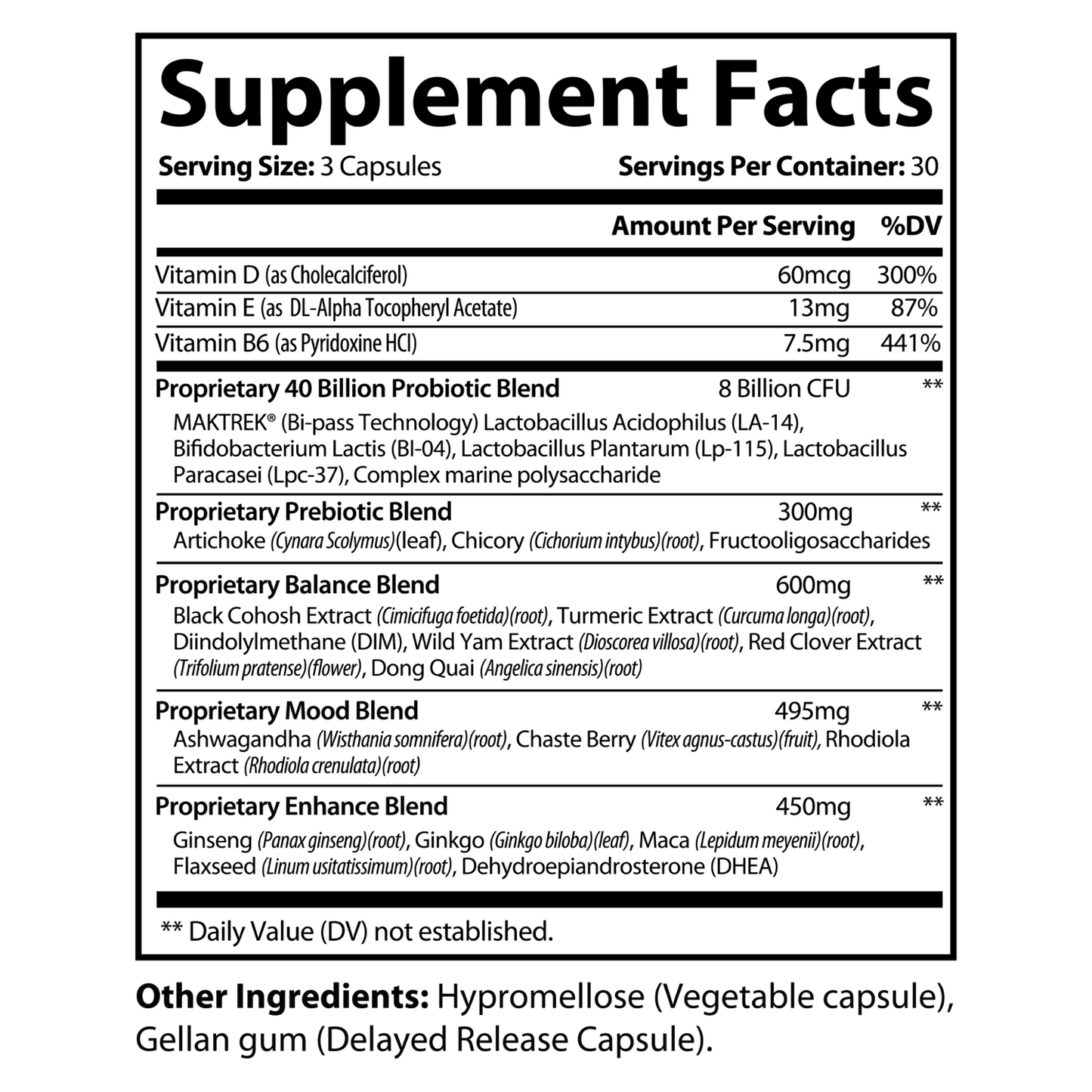
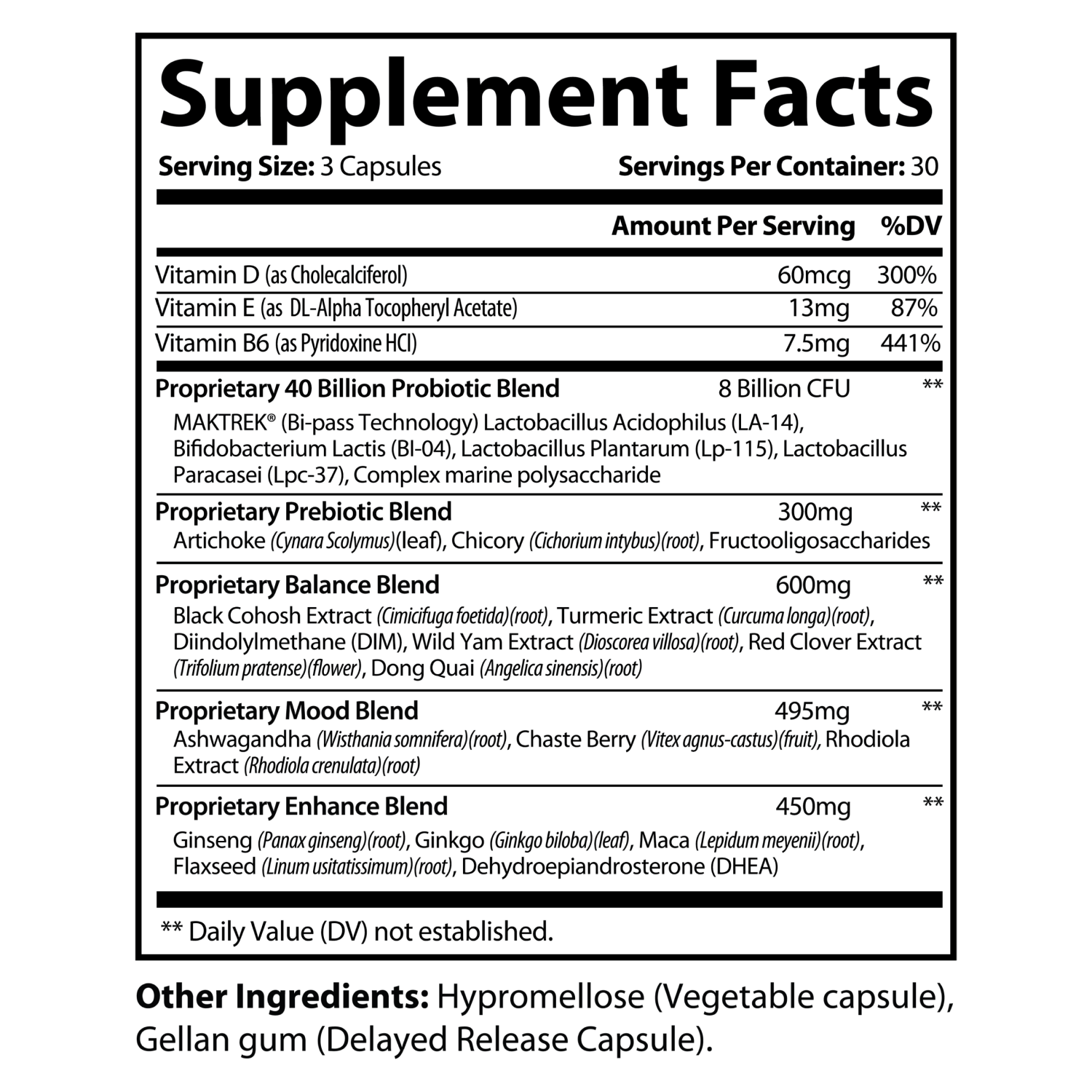
| Formula Ingredient Deck | Benefits of Each Ingredient |
| Vitamin D (as Cholecalciferol) – 60 mcg (300% DV) |
|
| Vitamin E (as DL-Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate) – 13 mg (87% DV) |
|
|
Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxine HCl) – 7.5 mg (441% DV) |
|
| 40 Billion Probiotic Blend – 8 Billion CFU |
|
| Prebiotic Blend – 300 mg |
|
| Balance Blend – 600 mg |
|
| Mood Blend – 495 mg |
|
| Enhance Blend – 450 mg |
|
Proper Use of This Supplement
Suggested Use: As a dietary supplement, take three (3) capsules once a day. For best results take 20–30 minutes before a meal with an 8 oz glass of water, or as directed by your healthcare professional.
| Our Formula vs. | Other Formulas in the Market |
| Third-party tested, USA made, GMP certified, FDA registered facility. | Others may source cheap raw materials without testing. |
| Uses advanced MAKTREK® probiotic delivery technology. | Other probiotics often degrade before reaching the gut. |
| Includes adaptogens and botanicals for mood and balance. | Many formulas exclude stress and mood support. |
| Comprehensive blend of probiotics, prebiotics, vitamins, and botanicals. | Most products focus only on one category of ingredients. |
References
- Holick, M. F. (2007). Vitamin D deficiency. The New England Journal of Medicine, 357(3), 266–281.
- Prietl, B., et al. (2013). Vitamin D and immune function. Nutrients, 5(7), 2502–2521.
- Rizvi, S., et al. (2014). The role of vitamin E in human health and disease. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 38, 25–36.
- Dakshinamurti, K. (2005). Vitamin B6 in metabolism and neurotransmitter function. Subcellular Biochemistry, 56, 151–166.
- Kennedy, D. O. (2016). B vitamins and the brain: Mechanisms, dose and efficacy. Nutrients, 8(2), 68.
- Martinsen, T. C., et al. (2016). Probiotic survival in gastrointestinal tract. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 22(3), 820–828.
- Ouwehand, A. C., et al. (2002). Probiotic and other functional microbes: From markets to mechanisms. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13(5), 483–487.
- Li, S. S., et al. (2021). Dietary fibers, prebiotics, and gut microbiota. Nutrients, 13(4), 1115.
- Slavin, J. (2013). Fiber and prebiotics: Mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients, 5(4), 1417–1435.
- Wuttke, W., et al. (2014). Phytotherapy of menopausal symptoms. Climacteric, 17(5), 485–492.
- Hewlings, S. J., & Kalman, D. S. (2017). Curcumin: A review of its’ effects on human health. Foods, 6(10), 92.
- Clarkson, T. B., et al. (2006). Effects of phytoestrogens on hormones. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 102(1-5), 201–208.
- Chandrasekhar, K., et al. (2012). A prospective, randomized trial of Ashwagandha root extract in reducing stress and anxiety. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 34(3), 255–262.
- Brown, R. P., et al. (2002). Rhodiola rosea: A phytomedicinal overview. HerbalGram, 56, 40–52.
- van Die, M. D., et al. (2009). Chaste tree for PMS and menopause. Phytomedicine, 16(1), 17–25.
- Kennedy, D. O., et al. (2001). Acute cognitive effects of ginseng. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 70(3), 505–514.
- Gertz, H. J., & Kiefer, M. (2004). Review about Ginkgo biloba extract in dementia. Pharmacopsychiatry, 37(4), 131–139.
- Gonzales, G. F., et al. (2001). Lepidium meyenii (Maca): A plant from the highlands of Peru. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 77(2-3), 165–174.
- Pan, A., et al. (2009). Effects of flaxseed and lignans on cardiovascular health and hormones. British Journal of Nutrition, 102(5), 939–954.
- Labrie, F. (1997). DHEA and its role in aging. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 828, 150–165.

Disclaimer
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.